Ontario, home to over 14 million people, has seen a significant shift in its crime landscape over the years. According to data from Statistics Canada, between 2007 and 2009, Ontario had one of the lowest violent and non-violent crime rates in Canada.
This introduction to Ontario’s crime statistics will explore the current state of crime across different regions, comparing urban centers like Toronto with rural areas. By examining the Crime Severity Index and other crime data, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of Ontario’s safety situation.
The analysis will cover various types of criminal activities and the factors influencing regional variations in crime rates, offering insights into how Ontario compares to other Canadian provinces.
Current Crime Rate Situation in Ontario
The current crime rate situation in Ontario presents a mixed picture. While some areas have seen a decrease in crime rates, others have experienced significant increases, highlighting the complexity of the issue.
Overview of 2023 Crime Statistics
In 2023, Ontario’s crime statistics revealed varying trends across different regions. The data shows that some cities like London experienced a 13.7% decrease in their Crime Severity Index, whereas regions like York saw a 15.2% increase. The Crime Severity Index is a crucial metric that measures the volume and severity of crime in a given area.
The crime rate per 100,000 population is another important indicator. In 2023, this rate varied significantly across Ontario, reflecting different crime patterns in urban and rural areas.

Key Indicators and Trends
Key indicators for measuring crime in Ontario include the Crime Severity Index, crime rates per 100,000 population, and the proportion of violent crimes versus property crimes. The data indicates that certain types of property crimes, such as theft and fraud, have evolved with changing technologies, posing new challenges for law enforcement.
Violent crime indicators demonstrate complex patterns across different communities. Some areas have seen increases in violent crime, while others have shown improvement, suggesting that localized factors play a significant role in crime trends.
| Region | Crime Severity Index Change | Violent Crime Rate | Property Crime Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| London | -13.7% | Decreased | Increased |
| York Region | +15.2% | Increased | Decreased |
| Ontario Average | +2.5% | Stable | Increased |
Crime Rate Ontario: Regional Breakdown
Regional crime rates in Ontario exhibit a diverse landscape, influenced by factors such as population density and policing strategies. Understanding these variations is crucial for developing effective crime prevention initiatives.
Greater Toronto Area Crime Statistics
The Greater Toronto Area (GTA) is a significant urban center with a high population density, which affects its crime statistics. The crime rate in Toronto is 69.2 per100,000 residents, with a notable presence of property crime, including theft and break-ins.
The GTA’s crime rate is influenced by its dense population and the resulting anonymity, which can contribute to higher rates of certain crimes.
Other Major Ontario Cities and Regions
Other major cities in Ontario, such as Ottawa, have different crime patterns. Ottawa’s crime rate is 55.8 per100,000 residents, indicating a relatively lower crime rate compared to Toronto.
Some smaller communities, however, experience higher crime rates. For instance, Kenora has a Crime Severity Index of 132.6, highlighting the challenges faced by rural areas.
Rural vs. Urban Crime Patterns
Rural and urban areas in Ontario demonstrate distinct crime patterns. Urban centers typically report higher volumes of property crime per100,000 residents, while rural communities face challenges with agricultural theft and longer police response times.
| Region | Crime Rate per100,000 | Crime Severity Index |
|---|---|---|
| Toronto | 69.2 | Low |
| Ottawa | 55.8 | Low |
| Kenora | High | 132.6 |
As illustrated in the table, the crime rate and Crime Severity Index vary significantly across different regions in Ontario. Understanding these differences is essential for tailoring crime prevention strategies to the specific needs of each area.
Violent Crime vs. Property Crime in Ontario
Understanding the dynamics between violent crime and property crime is crucial for grasping Ontario’s overall crime situation. Both types of crime have distinct trends and implications for public safety and law enforcement strategies.
Violent Crime Statistics and Trends
Violent crime in Ontario includes offenses such as homicide, assault, and robbery. The Crime Severity Index (CSI) is a key metric used to measure the severity of crimes, taking into account both the frequency and the seriousness of the offenses. According to recent statistics, some regions in Ontario have seen fluctuations in violent crime rates.
The violent crime rate per 100,000 population varies across different regions, with some areas experiencing higher rates than others. For instance, certain urban centers tend to have higher rates of violent crime compared to rural areas.
Property Crime Analysis
Property crime encompasses a range of offenses including theft, breaking and entering, fraud, and mischief. The data indicates that property crime rates also vary significantly across Ontario. For example, Toronto had a property Crime Severity Index of 59.1 (+17.8%), while the Greater Toronto Area was at 51.4 (+17.2%).
| City | Property Crime Severity Index | Change (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Toronto | 59.1 | +17.8% |
| Greater Toronto Area | 51.4 | +17.2% |
| Ottawa | 52.0 | +5.6% |
| Hamilton | 60.4 | +5.1% |
| London | 63.9 | -15.6% |
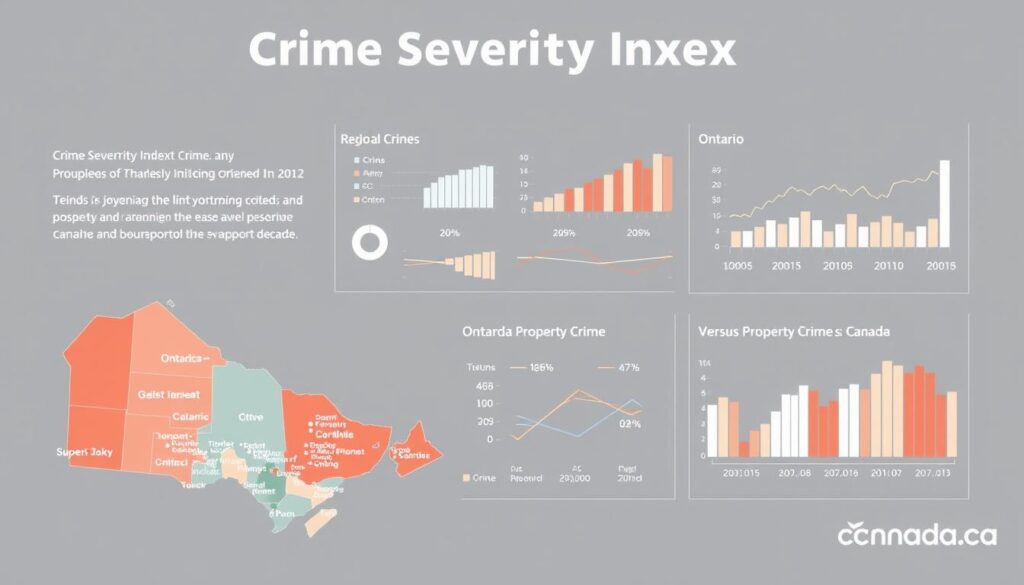
The relationship between property crime and economic factors is significant, with changes in unemployment rates, housing costs, and other economic indicators often correlating with fluctuations in property crime rates over time. Effective prevention strategies and policing approaches can successfully reduce property crime rates, as seen in cities like London, which experienced a 15.6% decrease.
Understanding the Crime Severity Index
The Crime Severity Index (CSI) is a sophisticated metric used by Statistics Canada to measure the relative severity of crime across different regions. Understanding crime rates in Ontario requires a deeper look into the Crime Severity Index, a crucial metric that provides insight into the province’s crime landscape.

How the Crime Severity Index Works
The CSI takes into account both the volume and severity of crime, assigning weights to different crimes based on their seriousness. For instance, violent crimes like homicide are given more weight than property crimes like theft. This approach provides a more comprehensive picture of crime than simply counting the number of crimes. According to Statistics Canada, the CSI is calculated based on data from police-reported crimes, ensuring that the index reflects the actual crime situation.
The Crime Severity Index is a valuable tool for comparing crime rates across different regions. By using the CSI, law enforcement agencies and policymakers can identify areas with higher crime severity and allocate resources accordingly.
Ontario’s Position in the National Rankings
Ontario generally maintains a relatively favorable position in national crime rankings, with its Crime Severity Index typically falling below the Canadian average. According to Statistics Canada data, Ontario’s crime rates per 100,000 population are often lower than those in western provinces like Saskatchewan and British Columbia. For example, the Greater Toronto Area had a Crime Severity Index of 58.5, significantly lower than Metro Vancouver’s 90.2. However, there are variations within Ontario, with some cities experiencing higher crime rates than the provincial average.
Understanding these variations is crucial for developing effective crime prevention strategies. By examining the Crime Severity Index, law enforcement agencies can identify trends and patterns in crime, enabling them to target their efforts more effectively.
Comparing Ontario’s Crime Rate to Other Provinces
Crime rates vary significantly across Canada, with Ontario exhibiting distinct trends compared to other provinces. Understanding these differences requires a closer look at provincial crime rate comparisons and the factors that influence regional variations.
Provincial Crime Rate Comparisons
Ontario’s crime rate is often compared to other provinces to understand its standing within Canada. The crime severity index is a crucial metric in these comparisons, as it takes into account the volume and severity of crimes reported. According to recent statistics, Ontario’s crime rate per 100,000 population is relatively moderate compared to other provinces. For instance, provinces like Saskatchewan and Manitoba have higher crime rates per 100,000, largely due to higher rates of violent crimes in certain areas.
- Ontario’s overall crime rate is influenced by its large and diverse population.
- The province experiences a mix of urban and rural crime patterns, affecting overall crime rates.
- Property crime remains a significant concern, particularly in urban centers.
Factors Influencing Regional Differences
Several factors contribute to the regional differences in crime rates across Canada. Socioeconomic conditions, including unemployment and income inequality, play a significant role in shaping crime trends. Additionally, the allocation of police resources and community-based crime prevention initiatives vary between provinces, influencing local crime rates.
- Demographic differences between provinces affect crime patterns, with age distribution and education levels being key factors.
- Geographic and environmental factors, such as the challenges faced by northern communities, also impact crime rates.
- The relationship between substance abuse and crime varies regionally, with different substances being more prevalent in different areas.
By examining these factors and comparing provincial crime rates, a clearer picture emerges of Ontario’s position within the Canadian context. This comparison not only highlights areas of concern but also informs crime prevention strategies tailored to specific regional needs.
Crime Code and Classification in Canada
Understanding the crime code and classification system in Canada is crucial for analyzing crime statistics and trends. The country’s justice system relies on a standardized framework for reporting and categorizing crimes, which is essential for informed decision-making and policy development.
The Canadian Criminal Code Framework
The Canadian Criminal Code provides the legal framework for defining and prosecuting crimes in Canada. It categorizes offenses into various groups, including violent crimes, property crimes, and other Criminal Code offenses. The Uniform Crime Reporting (UCR) Survey, managed by Statistics Canada, is the primary tool for collecting police-reported crime data. This survey categorizes criminal incidents into major groups, including violent crimes against persons, property crimes, and federal statute violations.
Key aspects of the UCR Survey include:
- Categorizing crimes into violent crimes, property crimes, and other offenses.
- Employing a “most serious offense” rule for incidents involving multiple offenses.
- Distinguishing between actual incidents and unfounded reports.
How Crimes Are Categorized and Reported
Crimes in Canada are categorized and reported through a systematic process. Police services across the country submit data using consistent definitions and categories, ensuring that crime statistics are reliable and comparable. The UCR Survey collects data through either the aggregate UCR Survey or the incident-based UCR2 Survey, with the latter providing detailed information about each criminal incident.
| Crime Category | Description | Reporting Method |
|---|---|---|
| Violent Crimes | Crimes against persons, including homicide and assault. | UCR2 Survey |
| Property Crimes | Theft, break and enter, and other property-related offenses. | Aggregate UCR Survey |
| Other Offenses | Mischief, disturbing the peace, and other Criminal Code offenses. | UCR2 Survey |
Recent initiatives by Statistics Canada and the Canadian Association of Chiefs of Police aim to enhance data collection, including information on the Indigenous and racialized identity of victims and accused persons. Understanding the methodological framework behind crime categorization and reporting is essential for interpreting crime statistics accurately.

Crime Prevention Initiatives in Ontario
Crime prevention in Ontario is a multifaceted approach that involves community programs, law enforcement strategies, and public education. This comprehensive strategy aims to address the root causes of criminal activity and enhance community safety.
Community-Based Prevention Programs
Community-based prevention programs play a crucial role in reducing crime in Ontario. These initiatives focus on addressing social issues such as substance abuse, poverty, and lack of education, which are often linked to criminal behavior. Programs targeting at-risk youth, for instance, provide them with alternatives to criminal activity, such as mentorship, education, and job training.
Law Enforcement Strategies
Law enforcement agencies in Ontario employ various strategies to prevent and combat crime. These include intelligence-led policing, community policing, and the use of technology to track and analyze crime trends. By adopting a proactive approach, law enforcement can more effectively deter criminal activity and respond to emerging threats.
Public Awareness and Education
Public awareness and education are critical components of crime prevention. Initiatives in this area focus on educating the public about crime trends, prevention strategies, and the importance of reporting suspicious activities. For example, campaigns on digital literacy and cybercrime prevention have become increasingly important as technology-facilitated crimes rise. Additionally, programs aimed at preventing property crime provide homeowners and businesses with practical strategies to protect their assets.
| Initiative Type | Description | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|
| Community Programs | Addressing social issues linked to crime | At-risk youth, communities |
| Law Enforcement | Intelligence-led and community policing | General public, law enforcement |
| Public Education | Crime trends, prevention strategies | General public, vulnerable populations |

Conclusion: The Future of Crime Rates in Ontario
The future of crime rates in Ontario is a pressing concern, with diverse trends emerging across different regions. As the province continues to grow and evolve, it’s essential to understand the factors influencing its crime landscape.
The crime severity index will remain a crucial tool in assessing the seriousness of criminal activity across Ontario. With varying trends observed across different areas, some experiencing increases in crime rates while others see decreases, the need for tailored approaches to crime prevention becomes evident.
Multiple factors will shape the future of crime in Ontario, including demographic shifts, economic conditions, and technological developments. The population growth, particularly in urban centers like the Greater Toronto Area, will influence crime rates per 100,000 residents, creating new public safety considerations.
To address these challenges effectively, Ontario will need to adopt integrated strategies that combine law enforcement, social services, and community engagement. By leveraging the crime severity index and other statistical measures, policymakers can develop evidence-based approaches to improve public safety across the province’s diverse communities.
Ultimately, the trajectory of Ontario’s crime rate will depend on the effectiveness of these strategies and the ability to adapt to emerging trends and challenges.

